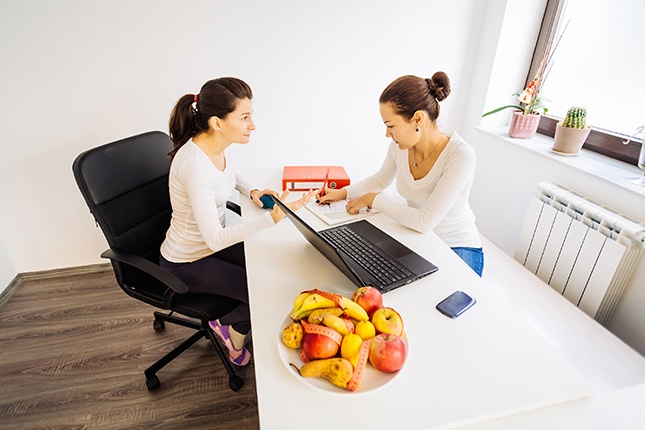
Nutrition and Health Coaching
At Modern Medicine, we’re passionate about using a collaborative approach to patient care, which is one of the many reasons why we use certified health coaches in our practices. Our health coaches go beyond simply teaching you about nutrition and exercise; they help inspire healthy behavior, which will truly take your health to the next level!
Thousands of our patients have had life-changing experiences through health coaching at Modern Medicine in Forney and Addison.

We have helped virtually all of these patients reach their health goals. In fact, some of these patients have become so passionate about their personal transformations that they feel the need to help others by becoming health coaches themselves!
At Modern Medicine, the practitioner, the health coach, and the patient all work together as a team to collectively create a treatment plan that fits your needs. We will meet you where you are by partnering with you on your journey to optimal health, and our health coaches are the key to making this partnership work!
We expect that your time spent with our health coaches will be a rewarding part of your experience here at Modern Medicine.
To learn more about the Modern Medicine approach to health coaching, read our FAQ below:
What Is Health Coaching?
Health coaching is the practice of utilizing informed planning, interventions, and strategies to instill healthy habits in patients to achieve an overall improvement in their daily lifestyle, wellness, and well-being.
At Modern Medicine, our health coaches work with patients who want to make lifestyle changes that can lead to weight loss, improved energy levels, a more balanced mood, and positive behavioral change. This type of coaching can be applied to individuals or groups. Each health coaching plan can also be customized to instill behavioral change that targets a specific goal, such as losing weight or quitting smoking.
Similar to how a sports coach can help maximize an athlete’s performance, a health coach will work one-on-one to help you develop the habits needed to excel at independently living a life towards improvement. Health coaches employ a similar process to talk therapy in that discussing ideas, approaching goals, and instilling habits will lead to an overall lifestyle change.
Health coaches can help patients develop new habits to improve many conditions related to health and physicality. Working with a health coach can help you:
- Lose weight
- Reduce stress
- Manage chronic health conditions
- Improve diet and exercise
- Quit smoking or tobacco
- Recover from addiction
- Adjust to a life-changing health event, such as a severe injury or a heart attack.
Who Can Benefit from Health Coaching?
You can benefit from the practices of health coaching if you have any of the following conditions:
- High blood pressure
- High blood sugar
- High cholesterol
- Symptoms of an underlying disease or health condition
- Dissatisfaction with life
- Unbalanced nutrition
- Overweight or obese
- Sleep deprivation
- Constant stress or anxiety
- Lack of time management
- Addiction
Does a Health Coach Replace Visits with My Doctor?
Although health coaches are effective at helping patients develop new habits that can lead to improved health and even healing, they should not be considered a replacement for a doctor’s treatment. Health coaches, although beneficial, are not medical providers and will not be able to diagnose or medically treat any symptoms. Rather than being considered as a replacement for medical treatment, health coaches should be considered a way to enhance your medical treatment, recovery, or healing process.
Health coaches can be a great way to close the gap between doctors and patients. For many patients who are in a recovery process, being at home and healing on your own can feel like a challenge. While you may not see your primary doctor until your next follow-up appointment, your health coach can be there to ensure you are on track at each step of your recovery process.
Schedule a Consultation with a Health Coach at Modern Medicine Today
If you’re ready to take your health to the next level, don’t hesitate to schedule a consultation with one of our health coaches at Modern Medicine. Experienced, qualified, and dedicated, our coaches are prepared to provide personalized treatment plans to help you become your healthiest. Click here or call 469-620-2054 (Dallas) / 972-552-2920 (Forney) to get in touch with our team in Texas today.